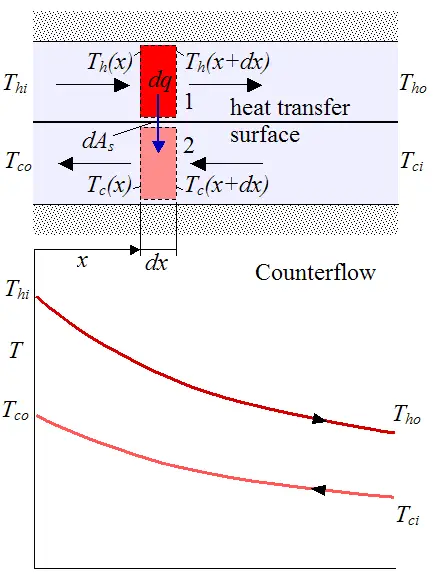
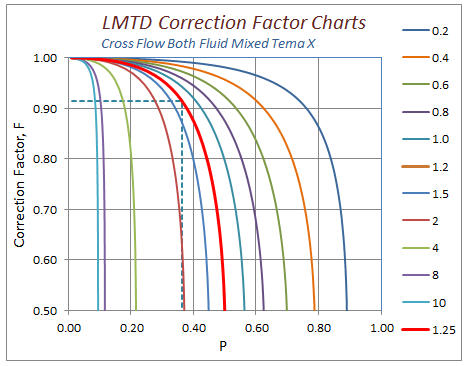
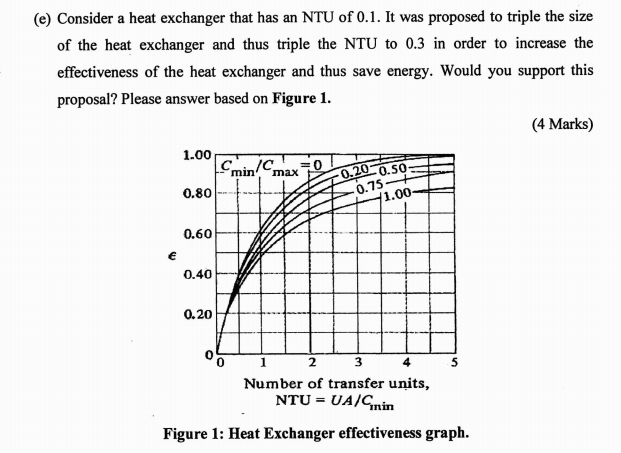
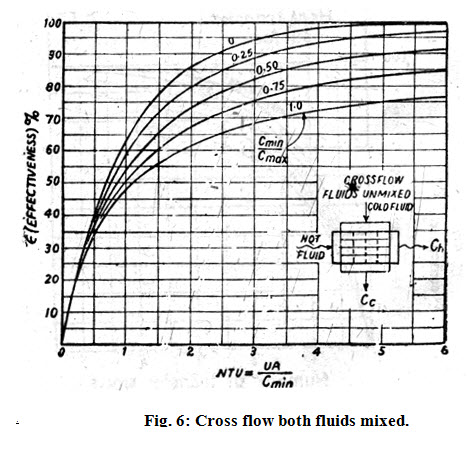
The number of transfer units ntu method is used to calculate the rate of heat transfer in heat exchangers especially counter current exchangers when there is insufficient information to calculate the log mean temperature difference lmtd.
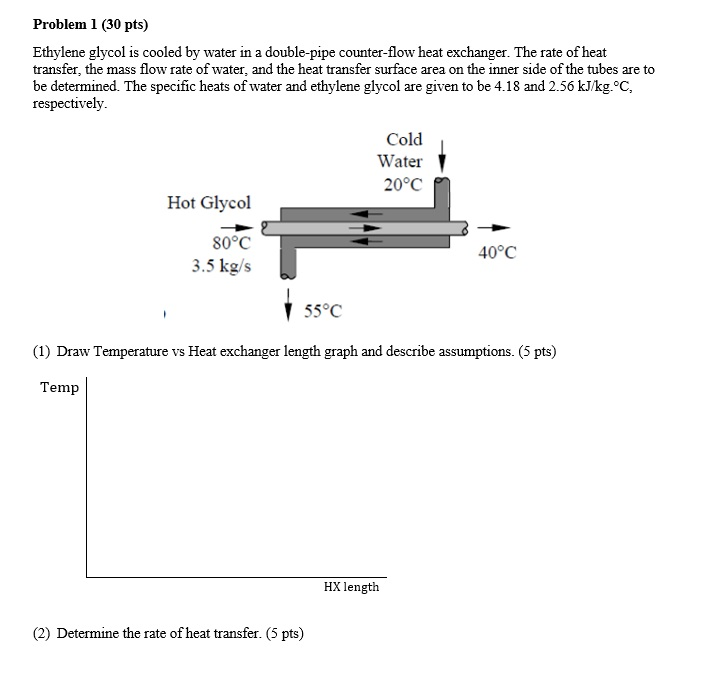
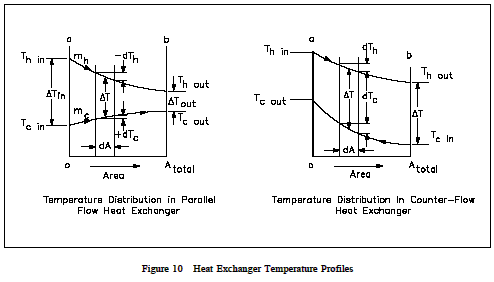
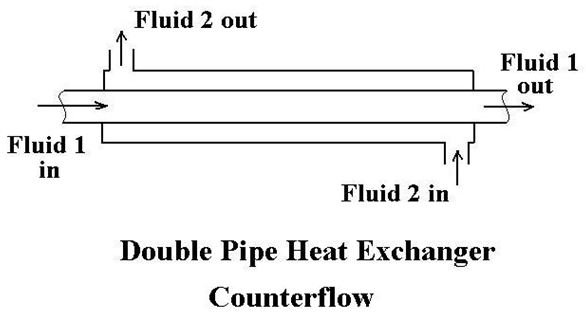
Counter flow heat exchanger graph.
A counterflow heat exchanger will require less heat exchange surface area than a parallel flow heat exchanger for the same heat transfer rate and the same inlet and outlet temperatures for the fluids.
The efficiency of a counter flow heat exchanger is due to the fact that the average t difference in temperature between the two fluids over the length of the heat exchanger is maximized as shown in figure 4 counter flow.
Energy balance of the hexagonal heat exchanger.
For example in a distillation column the vapors.
Crossflow parallel flow and counterflow heat exchanger configurations are three examples.
Countercurrent exchange is a mechanism occurring in nature and mimicked in industry and engineering in which there is a crossover of some property usually heat or some chemical between two flowing bodies flowing in opposite directions to each other.
Therefore the log mean temperature for a counter flow heat exchanger is larger than the log mean temperature for a similar.
A heat exchanger can have several different flow patterns.
In heat exchanger analysis if the fluid inlet and outlet temperatures are specified or can be determined by simple energy balance the lmtd method can.